varnish
varnish是一款高性能的开源http缓存加速器,缓存服务器我们最常见的是squid,这是一款较早期的较重量级的缓存的服务器,varnish与squid的关系就像现在的nginx和httpd的关系,现在nginx已经被广泛的接受了,所以相信varnish在未来的前途还是很可观的,在如今的互联网系统中,有太多的系统架构是依赖缓存服务器的,所以在整个系统架构中缓存是关键的一环,现在的互联网时代缓存为王,但想要管理好缓存也并不是容易办到的,缓存数据我们需要通过内核操控内存的中的数据,这对我们来说本身不可见,我们只能通过不断调试测试来完成缓存工作。
http cache
程序运行具有局部性特征:时间局部性,空间局部性,即每个程序在特定时间运行会较为频繁,当该时间点运行完的数据在下一刻可能仍会被需要运行,在该节点运行的数据,其周边的节点的运行的数据也会较为频繁。所以整个程序的运行是具有热点数据的,如果我们可以在整个系统中将热点数据进行缓存处理,那么整个系统中后端服务器的处理能力将会有指数级增长。
为了评定缓存的能力,我们有缓存命中率的评定标准(hit/(hit+miss)),缓存的命中率存在两种评定标准:
(1)文档的命中率:从命中的文档个数进行衡量
(2)字节的命中率:从命中的内容的大小进行衡量
对于缓存的整个处理步骤:
接受请求–>解析请求(提取请求的url及各种头部)–>查询缓存–>新鲜度检测–>构建响应报文–>发送响应–>记录日志
缓存控制机制:
1 | HTTP/1.0 Expires |
2 | Expires: Fri,20,May 2017 02:03:18 GMT #过期时间 |
3 | HTTP/1.1 Cache-Control: max-age |
4 | Cache-Control: no transform,max-age=3600 #相对时间,保存3600 |
5 | cache-request-directive= |
6 | no-cache |
7 | no-store |
8 | max-age |
9 | max-stale |
10 | min-fresh |
11 | cache-response-directive= |
12 | public |
13 | private |
14 | no-cache |
15 | no-store |
16 | must-revalidate |
17 | max-age |
18 | s-max-age |
新鲜度检测机制:
- 有效性再验证:revalidate
如果原始内容未改变,则仅响应首部(不用附带body部分):响应码为304(not modified)
如果原始内容发生了改变,则正常响应,响应码为200
如果原始内容消失,则响应为404,此时缓存中的缓存项也应该被删除 - 条件式请求首部
If-Modified-Since: 基于原始内容的最近一个修改的时间戳进行
If-Unmodified-Since:
If-Match
If-None-Match:基于Etag的比较进行
varnish进程特性
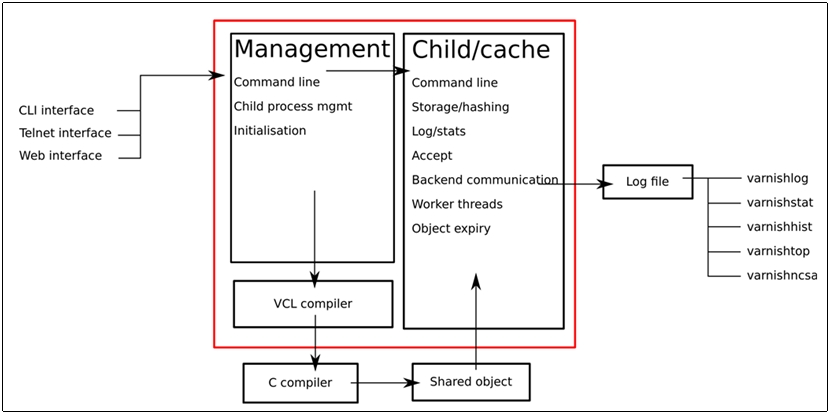
varnish的工作模式需要通过management提高的管理接口,通过vcl编程编译成c语言,再通过c编译成子进程可以识别的共享对象来进行配置。
- 安装
1 | ~]# yum install -y epel-release |
2 | ~]# yum install -y varnish |
- 配置varnish进程参数
1 | ~]# cat /etc/varnish/varnish.params |
2 | RELOAD_VCL=1 #是否运行reload |
3 | VARNISH_VCL_CONF=/etc/varnish/default.vcl #vcl配置文件 |
4 | # VARNISH_LISTEN_ADDRESS=192.168.1.5 #监听的ip |
5 | VARNISH_LISTEN_PORT=80 #监听的端口 |
6 | VARNISH_ADMIN_LISTEN_ADDRESS=127.0.0.1 #管理的ip |
7 | VARNISH_ADMIN_LISTEN_PORT=6082 #管理的端口 |
8 | VARNISH_SECRET_FILE=/etc/varnish/secret #认证文件 |
9 | VARNISH_STORAGE="malloc,256M" #varnish存储对象 |
10 | #VARNISH_STORAGE="file,/var/lib/varnish/varnish_storage.bin,1G" #varnish存储对象 |
11 | VARNISH_USER=varnish #varnish启动的用户 |
12 | VARNISH_GROUP=varnish #varnish启动的用户组 |
13 | #DAEMON_OPTS="-p thread_pool_min=5 -p thread_pool_max=500 -p thread_pool_timeout=300" #其他选项 |
14 | |
15 | |
16 | ~]# cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/varnish.service |
17 | ... |
18 | ExecStart=/usr/sbin/varnishd \ |
19 | -P /var/run/varnish.pid \ |
20 | -f $VARNISH_VCL_CONF \ |
21 | -a ${VARNISH_LISTEN_ADDRESS}:${VARNISH_LISTEN_PORT} \ |
22 | -T ${VARNISH_ADMIN_LISTEN_ADDRESS}:${VARNISH_ADMIN_LISTEN_PORT} \ |
23 | -S $VARNISH_SECRET_FILE \ |
24 | -s $VARNISH_STORAGE \ |
25 | $DAEMON_OPTS |
26 | ... |
varnish的存储对象:
(1)file :自管理的文件系统,黑盒:
(2)malloc:使用malloc()库调用在varnish启动时向内存申请指定大小的空间
(3)persistent:与file功能相同;仍处于测试期
启动varnish
1 | ~]# systemctl start varnish.service |
vcl
vcl是一种‘域‘专用的编程语言,vcl存在多个状态引擎,通过return的返回值来退出当前状态,并进入下个状态,彼此间状态相互联系,但彼此间又相互隔离,不同的状态引擎,其返回状态都不相同。
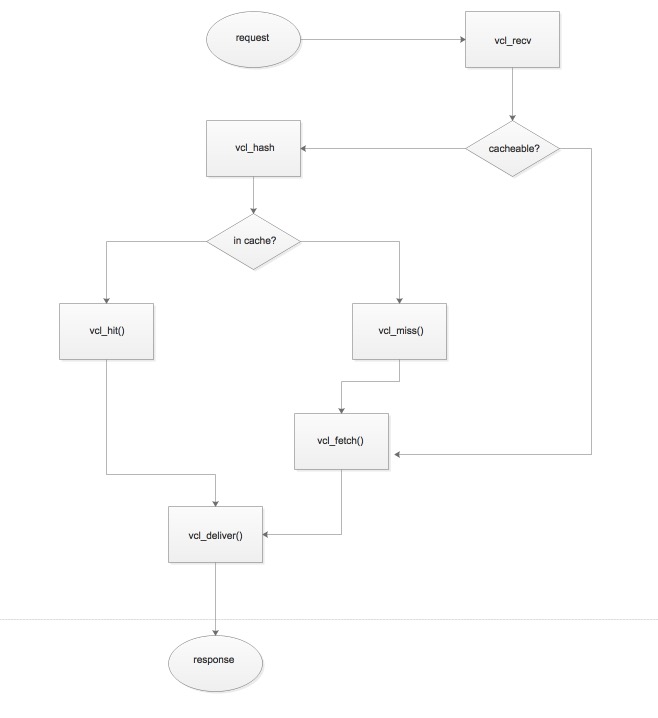
varnish的状态引擎:
1 | vcl_recv |
2 | vcl_hash |
3 | hit:vcl_hit |
4 | miss:vcl_miss |
5 | purge:vcl_purge |
6 | pipe:vcl_pipe |
7 | pass,hit_for_pass:vcl_pass |
8 | vcl_backend_fetch |
9 | vcl_backend_response |
10 | vcl_backend_error |
11 | |
12 | vcl_synth |
13 | |
14 | vcl_deliver |
各个状态引擎的关系如下图:
数据报文大致流向:
1 | vcl_recv-->vcl_hash--> |
2 | (1)vcl_hit--> |
3 | (a)vcl_deliver |
4 | (b)vcl_pass |
5 | (2)vcl_miss--> |
6 | (a)vcl_pass |
7 | (b)vcl_backend_fetch |
8 | (3)vcl_purge--> |
9 | (a)vcl_synth |
10 | (4)vcl_pipe--> |
11 | vcl_pass--> |
12 | vcl_backend_fetch |
13 | vcl_backend_fetch--> |
14 | vcl_backend_response-->vcl_deliver |
15 | vcl_backend_error |
vcl编程
varnish做反代,请求后端服务器
测试信息:
1 | ~]# cat /etc/varnish/default.vcl |
2 | vcl 4.0; |
3 | backend default { |
4 | .host = "10.211.55.43"; |
5 | .port = "80"; |
6 | } |
7 | sub vcl_deliver { |
8 | if (obj.hits>0) { |
9 | set resp.http.X-Cache = "HIT" + " " + server.ip; |
10 | } else { |
11 | set resp.http.X-Cache = "MISS" + " " + server.ip; |
12 | } |
13 | } |
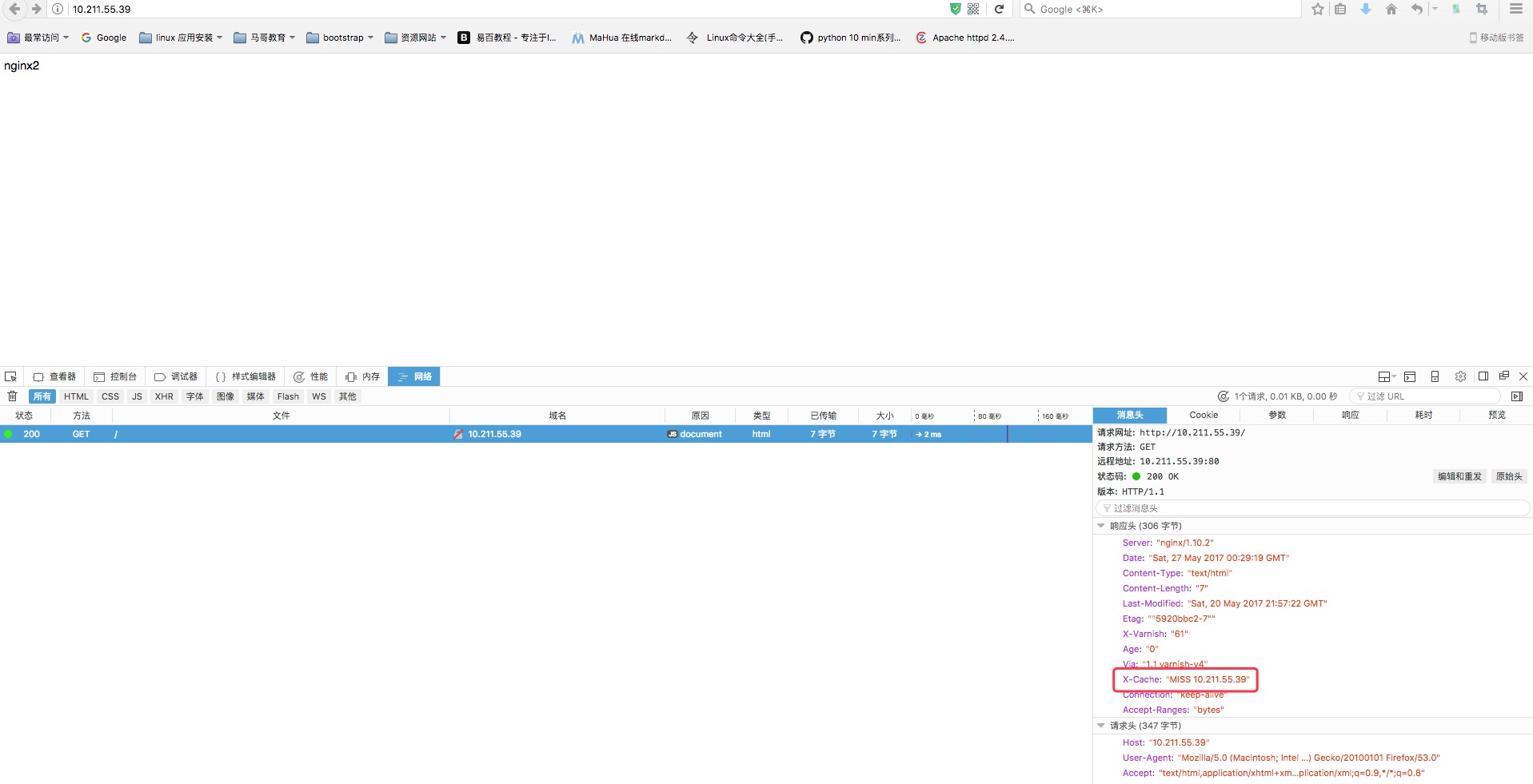
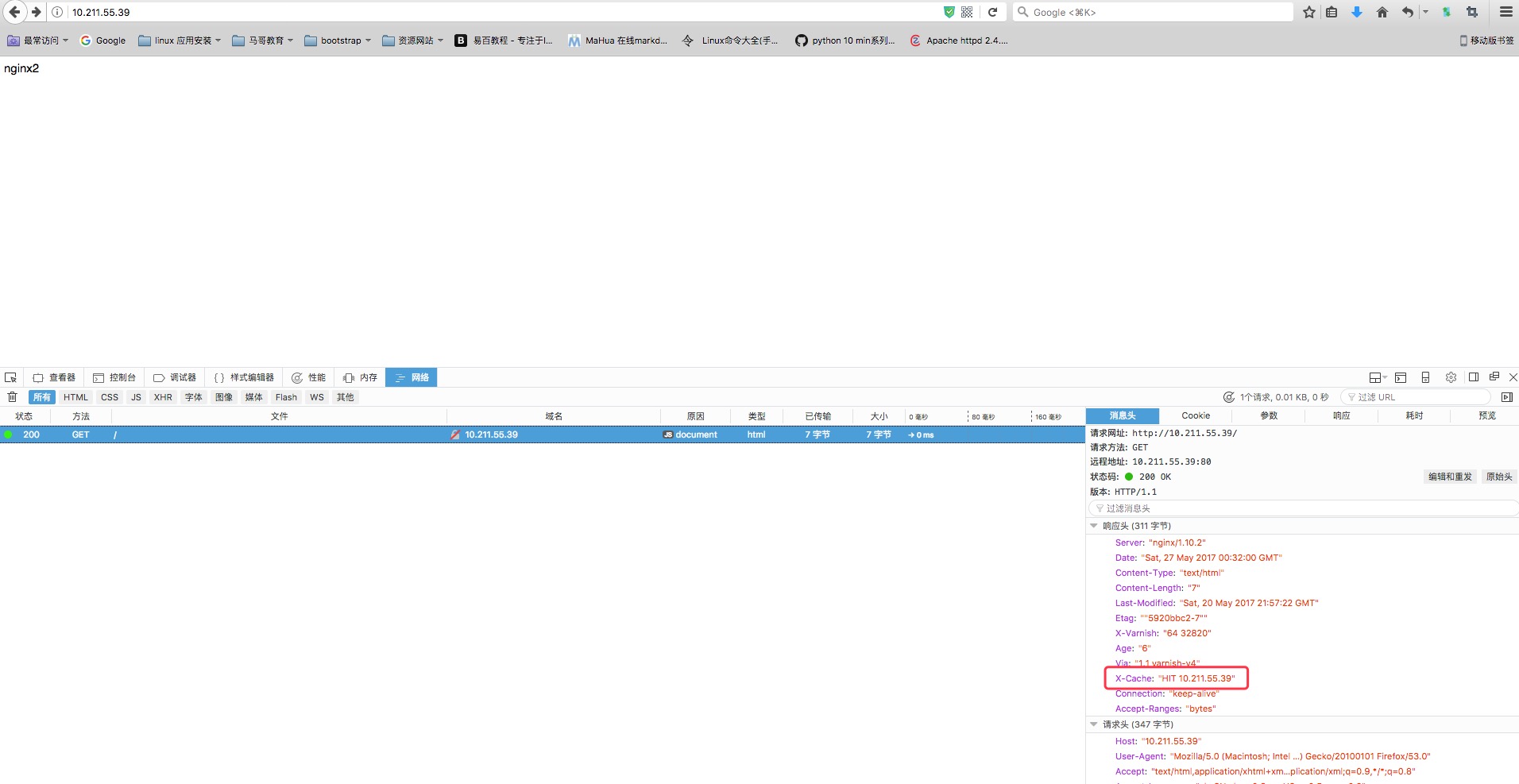
内建变量:
1 | req.*: 客户端请求 |
2 | req.http.*:客户端请求报文首部 |
3 | bereq.*: 由varnish向backend主机发出的http请求 |
4 | beresp.*:由backend主机发来的http响应报文 |
5 | resp.*:varnish响应client的http响应报文 |
6 | resp.http.*: 响应报文各首部的值 |
7 | obj.*:对缓存在缓存空间中的缓存对象属性,只读 |
8 | |
9 | client.*,server.*,storage.*: 可用在所有client side的sub routines中 |
自定义变量:set
常用的变量:
bereq.http.HEADERS
bereq.request: 请求方法
bereq.url:请求的url
bereq.poro: 协议版本
bereq.backend: 指明要调用的后端主机
beresp.poro
beresp.status: 响应的状态码
beresp.reason
beresp.backend.name
beresp.http.HEADERS
beresp.ttl:后端服务器响应内容的余下的生存时间
obj.hits: 此对象从缓存中命中的次数
obj.ttl: 对象ttl值
server.ip
server.hostname
req.method:请求方法
req.url:请求的url
实例1
强制对某资源请求不检查缓存:
1 | vcl 4.0; |
2 | backend default { |
3 | .host = "10.211.55.43"; |
4 | .port = "80"; |
5 | } |
6 | sub vcl_recv { |
7 | if(req.url ~ "(?!)/admin | (?!)/login") { |
8 | return(pass) |
9 | } |
10 | } |
varnish不能随便重启,我们需要通过管理接口重新加载配置:
1 | ~]# varnishadm -S /etc/varnish/secret -T 127.0.0.1:6082 |
2 | 200 |
3 | ----------------------------- |
4 | Varnish Cache CLI 1.0 |
5 | ----------------------------- |
6 | Linux,3.10.0-514.16.1.el7.x86_64,x86_64,-smalloc,-smalloc,-hcritbit |
7 | varnish-4.0.4 revision 386f712 |
8 | |
9 | Type 'help' for command list. |
10 | Type 'quit' to close CLI session. |
11 | |
12 | vcl.load test /etc/varnish/default.vcl |
13 | 200 |
14 | VCL compiled. |
15 | |
16 | vcl.use test |
17 | 200 |
18 | VCL 'test5' now active |
实例2
对公开的图片取消其私有标识,并强行通过varnish修改的时长
1 | vcl 4.0; |
2 | backend default { |
3 | .host = "10.211.55.43"; |
4 | .port = "80"; |
5 | } |
6 | |
7 | sub vcl_backend_response { |
8 | if(beresp.http.cache-control !~ 's-maxage') { |
9 | if(bereq.url ~ "(?!)\.jpg$") { |
10 | set beresp.ttl = 7200s; |
11 | unset beresp.http.Set-Cookie; |
12 | } |
13 | if(bereq.url ~ "(?!)\.css") { |
14 | set beresp.ttl = 3600s; |
15 | unset beresp.http.Set-Cookie; |
16 | } |
17 | } |
18 | } |
实例3
缓存修剪
1 | vcl 4.0; |
2 | backend default { |
3 | .host = "10.211.55.43"; |
4 | .port = "80"; |
5 | } |
6 | |
7 | acl purgers { |
8 | "127.0.0.1"; |
9 | "10.211.55.0"/24; |
10 | } |
11 | |
12 | sub vcl_recv { |
13 | if(req.method == "PURGE") { |
14 | if(!client.ip ~ purgers) { |
15 | return(synth(405,"purger not to alloed to " + client.ip)); |
16 | } |
17 | return(purge); |
18 | } |
19 | } |
20 | |
21 | sub vcl_purge { |
22 | return(synth(200,"purged")); |
23 | } |
测试:
1 | ~]# curl -X PURGE http://10.211.55.39 |
2 | <!DOCTYPE html> |
3 | <html> |
4 | <head> |
5 | <title>200 purged</title> |
6 | </head> |
7 | <body> |
8 | <h1>Error 200 purged</h1> |
9 | <p>purged</p> |
10 | <h3>Guru Meditation:</h3> |
11 | <p>XID: 32791</p> |
12 | <hr> |
13 | <p>Varnish cache server</p> |
14 | </body> |
15 | </html> |
16 | |
17 | 不在acl列表中使用purge |
18 | ~]# curl -X PURGE http://10.211.55.39 |
19 | <!DOCTYPE html> |
20 | <html> |
21 | <head> |
22 | <title>405 purger not to alloed to 10.212.55.43</title> |
23 | </head> |
24 | <body> |
25 | <h1>Error 405 purger not to alloed to 10.212.55.43</h1> |
26 | <p>purger not to alloed to 10.212.55.43</p> |
27 | <h3>Guru Meditation:</h3> |
28 | <p>XID: 32799</p> |
29 | <hr> |
30 | <p>Varnish cache server</p> |
31 | </body> |
32 | </html> |
实例4
设定多个后端主机
1 | vcl 4.0; |
2 | backend default { |
3 | .host="10.211.55.34", |
4 | .port="80", |
5 | } |
6 | |
7 | backend appser { |
8 | .host="10.211.55.35"; |
9 | .port="80"; |
10 | } |
11 | |
12 | sub vcl_recv { |
13 | if(req.url ~ "(?!)\.php$") { |
14 | set req.backend_hint = appser; |
15 | } else { |
16 | set req.backend_hint = default; |
17 | } |
18 | } |
实例5
负载均衡器
1 | vcl 4.0; |
2 | import directors |
3 | |
4 | backend default { |
5 | .host="10.211.55.34"; |
6 | .port="80"; |
7 | .probe={ |
8 | .url="/"; |
9 | .interval=1s; |
10 | .window=8; |
11 | .threshold=5; |
12 | .timeout=2s; |
13 | } |
14 | } |
15 | |
16 | backend appser { |
17 | .host="10.211.55.35"; |
18 | .port="80"; |
19 | .probe={ |
20 | .url="/"; |
21 | .interval=1s; |
22 | .window=8; |
23 | .threshold=5; |
24 | .timeout=2s; |
25 | } |
26 | } |
27 | |
28 | sub vcl_init { |
29 | new bar=directors.round_robin(); |
30 | bar.add_backend(default); |
31 | bar.add_backend(appser); |
32 | } |
33 | |
34 | sub vcl_recv { |
35 | set req.backend_hint=bar.backend(); |
36 | } |
测试:
1 | ~]# curl 10.211.55.39 |
2 | nginx1 |
3 | ~]# curl 10.211.55.39 |
4 | nginx2 |
varnish常用的命令行工具
varnishadm: varnish命令行管理接口
varnishtop: varnish实时请求状态查看
varnishncsa: varnish格式化请求日志查看,默认在内存中只有90m的存储空间,需要实时写入存储,可以启动varnishncsa.service
varnishlog: varnish原始日志查看,可以启动varnishlog写入存储
varnishstat: varnish状态查看

